CLEAR item#25
“Feature extraction method. Indicate which software programs or tools are used for radiomic feature extraction. Specify the version of the software and the exact configuration parameters (also see Item#55). Provide reference and web link to the software. Indicate if the software adheres to the benchmarks/certification of IBSI. Specify the general feature types, such as deep features, hand-crafted features, engineered features, or a combination. Refer to the mathematical formulas of the hand-crafted and engineered features. Provide formulas and code if new hand-crafted features are introduced. Present the architectural details for deep feature extraction. Provide details of any feature engineering performed. Specify whether radiomic features are extracted in a two-dimensional (2D) plane, 2D tri-planar, or three-dimensional (3D) space. If 2D features are extracted from 3D segmentation, provide reasons (e.g., large slice thickness) as to why such an approach is followed.” [1] (from the article by Kocak et al.; licensed under CC BY 4.0)
Reporting examples for CLEAR item#25
Example#1. “The open-source python package for the extraction of radiomic features from medical imaging Pyradiomics (version 2.2.0) was used to extract the radiomic feature.” [2] (from the article by Bartholomeus et al.; licensed under CC BY 4.0)
Example#2. “Following manual segmentation, images were exported to the Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative (IBSI) compliant software SOPHiA DDMTM Radiomics (Sophia Genetics).” [3] (from the article by Feliciani et al.; licensed under CC BY 4.0)
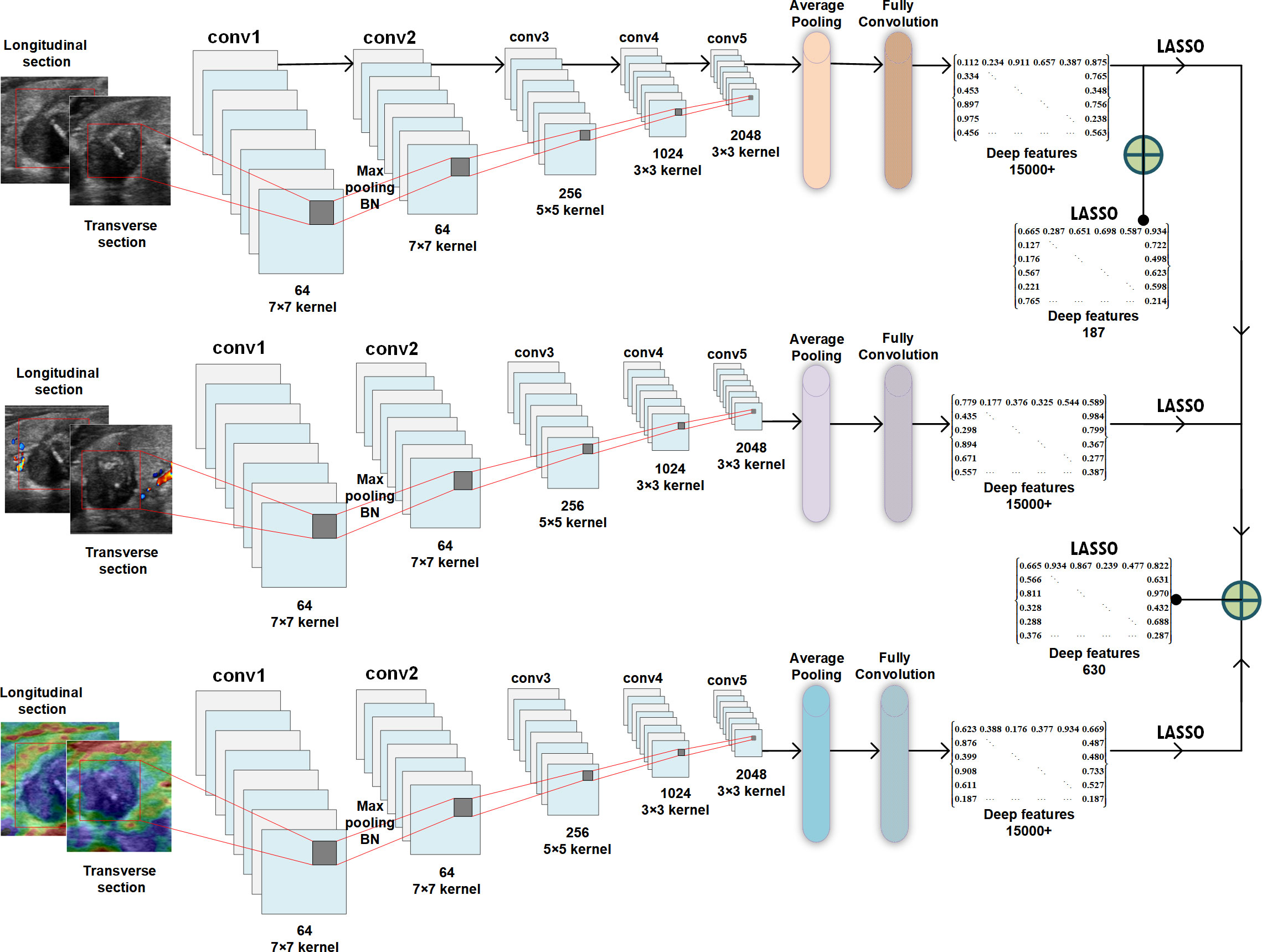
Example#3. See Figure 1.
Figure 1. “Schematic of deep feature extraction, selection, and fusion for the ResNet50 network.” [4] (from the article by Dai et al.; licensed under CC BY 4.0)
Explanation and elaboration of CLEAR item#25
Item#25 explores the feature extraction methodology, a pivotal step involving the identification of previously unseen image patterns through the utilization of agnostic or non-semantic features [5]. The authors are encouraged to clearly specify the software programs, versions, and exact configuration parameters for radiomic feature extraction to guarantee methodological transparency, quality control and effective troubleshooting [6]. Several platforms are available, some of them are IBSI compliant. Among the available platforms for the features extraction PyRadiomics, LIFEx, and CERR are IBSI-compliant, whereas, for instance, IBEX is not [7]. Furthermore, the authors should furnish information on general feature types, providing formula and code, to enhance reproducibility and facilitate a more informed interpretation of the study’s results. Additionally, when incorporating deep features, authors are advised to present the architectural details of their extraction process, preferable with an illustration such as in Example#3 or textually. These considerations collectively contribute to the credibility and reliability of radiomics research.
References
- Kocak B, Baessler B, Bakas S, et al (2023) CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics research (CLEAR): a step-by-step reporting guideline for authors and reviewers endorsed by ESR and EuSoMII. Insights Imaging 14:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13244-023-01415-8
- Bartholomeus GA, van Amsterdam WAC, Harder AM den, et al (2023) Robustness of pulmonary nodule radiomic features on computed tomography as a function of varying radiation dose levels-a multi-dose in vivo patient study. Eur Radiol 33:7044–7055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-09643-8
- Feliciani G, Serra F, Menghi E, et al (2023) Radiomics in the characterization of lipid-poor adrenal adenomas at unenhanced CT: time to look beyond usual density metrics. Eur Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-10090-8
- Dai Q, Tao Y, Liu D, et al (2023) Ultrasound radiomics models based on multimodal imaging feature fusion of papillary thyroid carcinoma for predicting central lymph node metastasis. Front Oncol 13 https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1261080
- Koçak B, Durmaz EŞ, Ateş E, Kılıçkesmez Ö (2019) Radiomics with artificial intelligence: a practical guide for beginners. Diagn Interv Radiol Ank Turk 25:485–495. https://doi.org/10.5152/dir.2019.19321
- Mayerhoefer ME, Materka A, Langs G, et al (2020) Introduction to Radiomics. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med 61:488–495. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.118.222893
- Fornacon-Wood I, Mistry H, Ackermann CJ, et al (2020) Reliability and prognostic value of radiomic features are highly dependent on choice of feature extraction platform. Eur Radiol 30:6241–6250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-06957-9